Categories
Tags
-
#air compressor
#Double Wire Fence
#Malleable Iron Pipe Fittings
#hollow brick machine
#Filter Press
#laminate wood flooring
#seamless steel pipe
#Current Transformer
#Eccentric Butterfly Valve
#Aluminum Casting
# Control Valve Market
#adult diapers
#four way pipe fitting
#block machine for sale in usa
#24 inch butterfly valve
#8 inch butterfly valve
#8 inch butterfly valve price
#black pipe y fitting
#China non woven fabric Supplier
#monitor wa fire
#underground gate valve
#China Sprocket supplier
#office table for 4 person
#Automatic Filter Presses
#door manufacturers in china
#China wholesale iron doors manufacturers
#1610 co2 Non-metallic laser cutting machine for wood
#China Adult diaper pants manufacturer
#glass office partition walls
#china pipe fitting
#filter press plate
#silicone heater hose
#CATERPILLAR Excavator Carrier Roller
#China wet wipes manufacturing machine
#China ceramic fiber blanket manufacturer
#pallet coil nails
#Newly Designed Wafer Butterfly Valves for Long Life-Period
#membrane switch supplier
#8 pump
#adult diaper websites
#L-muscone supplier price in China
#French Exterior Double Glass Wrought Iron Doors
#ECO Customized Colors Personalized Grocery Bag PP Nonwoven Flat Bag
#silicone tubing suppliers
#cubicle desk organizer
#Steel Bar Grating manufacturer
#HITACHI EX120 Excavator Undercarriage Part Carrier Roller
#Partition Workstation hot sale in China
#membrane switch panels
#Excavator Undercarriage Part Carrier Roller
#cnc wood carving machine
#China Baby diaper pants factory
#coat buttons metal supplier
#ceramic fire board
#China 11.2 inch 20 gauge fine wire staples
#heart shaped pin badges clasp
#reflective road studs supplier
#china office table prices
#180 Degrees Silicone Hose
#triple offset butterfly valve
#China best wet wipes for face manufacturer
#baby diaper online sale
#wall saw blade
#aluminum silicate ceramic
#vacuum formed shapes
#China fiber laser cleaning machine for sale
#beauty bag factories
#carrier roller suppliers
#China danfoss h1b suppliers
#the maker mini laser engraver
#black pipe fitting
#custom metal tags for clothing
#6 piece bedding set
#China L-muscone supplier price
#Fiber laser machine manufacturers
#plush bath towels,white wash cloths,white wash cloth,100 cotton towels,organic washcloths wholesale
#cozy blanket,woven blankets,Green Throw Blanket,purple velvet throw blanket
#gray bedding set,Halloween Bedding Set,cartoon bedding sets,Bohemian Bedding Set
#parker pv080 piston pump
#china rod ends manufacturer
#servo hydraulic testing machine
#best metal laser engraver
#rollers for track
#china car part manufacturers
#China brick machines
#plastic coated chicken wire
#China KOMATSU PC300-7 Excavator Undercarriage Part Carrier Roller
#traffic cone manufacturers
#China adult diaper manufacturer
#non rising stem resilient seated gate valve
#reslient seat gate valve
#HITACHI DX370 Excavator Undercarriage Part Sprocekt
#Nonwoven Tote Bag
#china Φ20 Rain Hose 0.15mm supplier
#Isobutylbenzene supplier
#china fire foam monitor manufacturer
#raised reflective pavement markers
#engine crane
#bi pipe fittings
#heavy piece of metal with tag
#excavator track rollers for sale
#fire ground monitor
#wipes packaging
#high speed adult diaper machine
#diaper machine manufacturers
#polytunnel greenhouse
#soy sauce
#90903 63014
#fire sprinkler fittings
#drill bit spanish
#China overhead bridge crane
#Jingjin filter press
#black industrial piping
#reflective studs
#diaper machine story
#galvanized tee fittings
#portable track press
#China Alkanes suppliers
#wall cutting blade
#ceramic tile cutter blade
#lug vs wafer butterfly valve
#GI Pipe fittings
#upper track rollers for sale
#cnc leather
#flash point of oil
#generator radiator
#vibration knife cutting systems
#electric hoist
#floor jack
#bspt vs npt
#palet jack
#diaper procedure
#auto transmission temperature sensor
#field fence for goats
#concrete core bits
#manual chain hoist
#open cup flash point
#erw pipe
#waist bag outdoor
#marble cutting blade
#wholesale music instruments
#fiberglass cutting machine
#fire sprinkler control valve
#concrete cutting blade
#drum sets
#nappy making machine
#track tensioner assembly
#brushless motor drawing
#bulldozer track
#cellular health supplement
#fire sprinkler check valve
#Miniature Bed
#oliver valves
#sling
#Manual Fire Water Monitor
Archives
What’s the Function of NPSF, NPS, NPT & NPTF?
-
Why Thread Standards Matter?
Thread standards protect the safety of a piping system. Each standard controls shape, pitch, sealing style, and tolerance. These factors affect flow, pressure retention, and leak resistance. Even small changes in thread form can change the performance of a joint. Many fitting types use these threads, so knowing the function of each type helps you make better choices.
What NPS Threads Do?
NPS means National Pipe Straight. These threads stay straight from end to end. They do not seal by themselves. Installers use gaskets or sealing compounds to stop leaks. NPS threads guide the pipe into a fitting with stable alignment. This makes them ideal for low-pressure tasks and mechanical connections. These threads offer smooth assembly and simple maintenance.
How NPSF Threads Work?
NPSF uses straight internal threads. These threads work with external dryseal threads like NPTF. NPSF threads hold the male thread steady and help the system seal under pressure. They shape the contact surface so the external thread compresses correctly. This compression creates a tight seal without heavy use of extra sealant. NPSF threads appear in fluid control systems where safety matters.
The Core Function of NPT Threads
NPT stands for National Pipe Taper. These threads narrow slightly toward the end. The taper helps the threads compress as they tighten. This compression forms the seal. NPT threads work well in gas, water, and oil systems. They are common across many industries. Users like the simple design and high seal strength. Many installations still use tape or compound for added security.
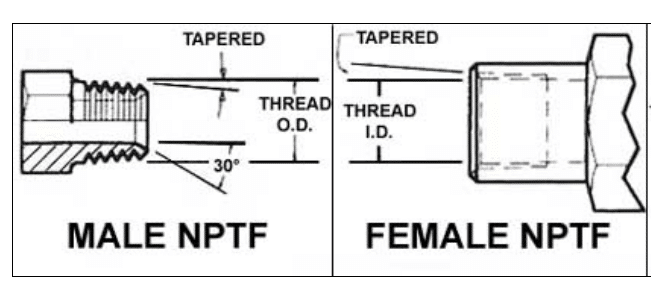
What NPTF Threads Are Designed to Do?
Many people search what is nptf thread because NPTF is different from NPT. NPTF means National Pipe Taper Fuel. It is also known as a dryseal type. It looks like NPT but offers a tighter fit. The thread roots and crests fill the gaps between the male and female parts. This reduces voids inside the joint. A correct NPTF fit creates a seal without extra tape. Many pressure systems prefer this style for cleaner installation.
Why These Threads Cannot Replace Each Other?
Each thread type has strict dimensions. Even small changes affect the seal. A straight thread does not match a taper thread. A dryseal type does not work with a non-dryseal system in high pressure tasks. NPSF pairs with NPTF because of internal and external fit. NPS works best with fittings using separate sealing parts. Mixing thread types causes leaks, stress failures, or poor alignment. Installers must choose based on the task, not convenience.
How to Identify Each Thread Type?
Installers check diameter, taper, and pitch. A straight thread keeps the same diameter along its length. A taper thread becomes smaller toward the end. Dryseal threads show tighter tolerances. Many users measure with gauges to confirm the type. When users study what is nptf thread, they often learn that NPTF gauges differ from NPT gauges. The correct gauge ensures safe installation.
Why Seal Quality Differs Between Standards?
Seal performance depends on how threads contact each other. Straight threads do not compress, so they rely on a separate seal. Taper threads compress by design. Dryseal taper threads compress even more because the thread shapes remove clearance. Each type offers different leakage control. You must match the thread to the pressure level and fluid type.
Where NPS Threads Are Common?
NPS threads fit tasks where alignment matters more than sealing. They appear in mechanical joints, low-pressure valves, and structural connections. Installers like NPS because it is easy to assemble and does not deform under pressure. This makes it reliable for systems that need regular maintenance.
Where NPSF Threads Are Used?
NPSF threads support precise sealing jobs. They match with NPTF male threads for high-pressure systems. Many fuel systems, hydraulic tools, and fluid transfer lines use NPSF. These threads stay stable even under temperature shifts. Installers trust them because they allow dryseal functions without extra steps.
Where NPT Threads Work Best?
NPT threads are common in water lines, air systems, and light fuel tasks. They offer strong grip and good sealing. Many old and new systems use NPT because it is easy to produce and simple to understand. Even today, many fitting types rely on NPT threads for daily operation.
Where NPTF Threads Are Preferred?
NPTF threads appear in high-pressure fuel lines and clean fluid systems. They prevent leaks even when the system faces vibration or thermal change. Dryseal structures reduce the need for tape. This makes the joint cleaner and stronger. Many designers prefer NPTF when safety rules require a zero-leak joint.
How Tolerance Affects Thread Performance?
Thread tolerance controls the gap between male and female parts. Straight threads use aligned walls for guidance. Taper threads use angled walls for sealing. Dryseal threads use high accuracy to close gaps. Too much tolerance creates leaks. Too little tolerance makes assembly hard. Installers check tolerance to keep the system safe.
Why Material Matters for Threads?
Metal hardness changes how threads behave. Softer metals compress more. Harder metals resist compression. Straight threads work well with many materials. Taper threads need balanced hardness to form a safe seal. Dryseal threads need enough strength to hold shape under pressure. Choosing the right material helps each thread perform well.
How Pressure Levels Shape Thread Selection?
Pressure determines which thread type to use. Low pressure systems can use straight threads with seals. Medium pressure tasks work well with NPT. High pressure jobs may need NPTF. When people learn what is nptf thread, they often discover it was created for high-pressure fuel. This is why correct selection protects the system from failures.
How Temperature Affects Thread Performance?
Heat expands metal. Cold contracts metal. A taper thread handles temperature change better because of the compression pattern. Straight threads rely on seals that must resist heat. Dryseal threads need stable materials for zero gap performance. Designers choose the right type to prevent leaks caused by thermal shift.
How Fitting Types Influence Thread Choice?
Different fittings require different threads. Some fittings need fast assembly. Some handle vibration. Some protect high-pressure flow. Straight threads help alignment. Taper threads help sealing. Dryseal threads help safety. When you understand each function, you choose the right style for any fitting.
How to Ensure a Leak-Free Joint?
Installers check surface quality, pitch, and taper. They tighten the joint with care to avoid damage. For NPT joints, they use the right sealing tape. For NPTF joints, they inspect the thread form to ensure dryseal action. Each step helps the system stay safe and leak-free.
How Designers Use These Thread Standards?
Designers select threads early in the planning stage. They consider fluid type, pressure, vibration, and service life. They avoid mixing standards. Many design notes reference thread choice as a key factor in performance. A clear understanding of each thread style helps create better systems.
Final Thoughts on NPS, NPSF, NPT & NPTF
Each thread type serves a purpose. NPS aligns. NPSF supports dryseal tasks. NPT seals through taper. NPTF seals with extra precision.
